Therapeutic
Hypothesis
Mechanistic Rationale
HDAC6 inhibitor treatment has the potential to preserve axonal transport to stop or slow the progression of ALS and AD and may prevent tau aggregation and stop or slow the progression of AD
Mechanistic Rationale
HDAC6 inhibitor treatment has the potential to preserve axonal transport to stop or slow the progression of ALS and AD and may prevent tau aggregation and stop or slow the progression of AD
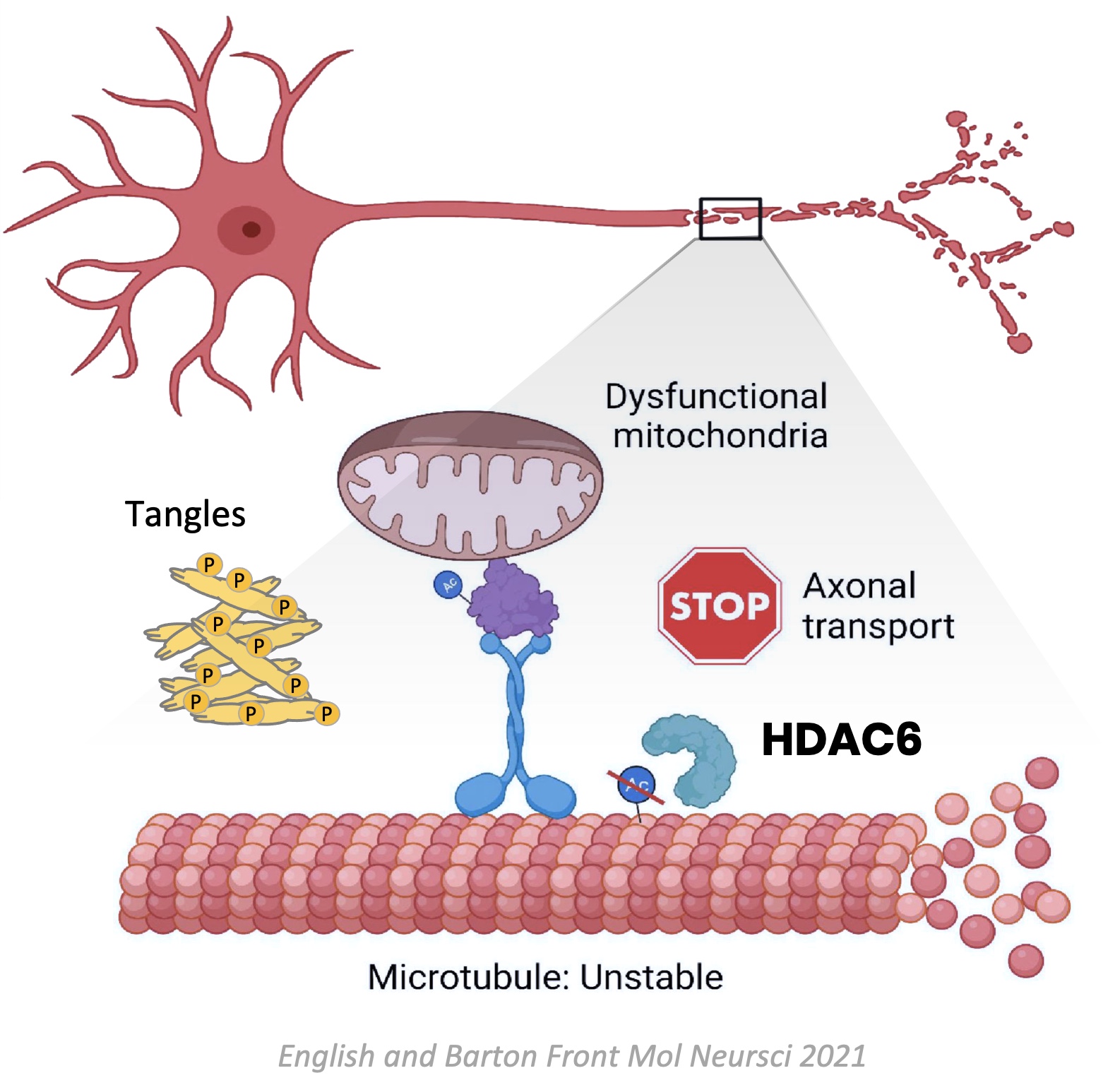
Acetylated tubulin, tau and Miro1 proteins provide structure to microtubules and support axonal transport.
HDAC6 deacetylates tubulin, tau and Miro1 which makes microtubules less resilient and disrupts axonal transport.
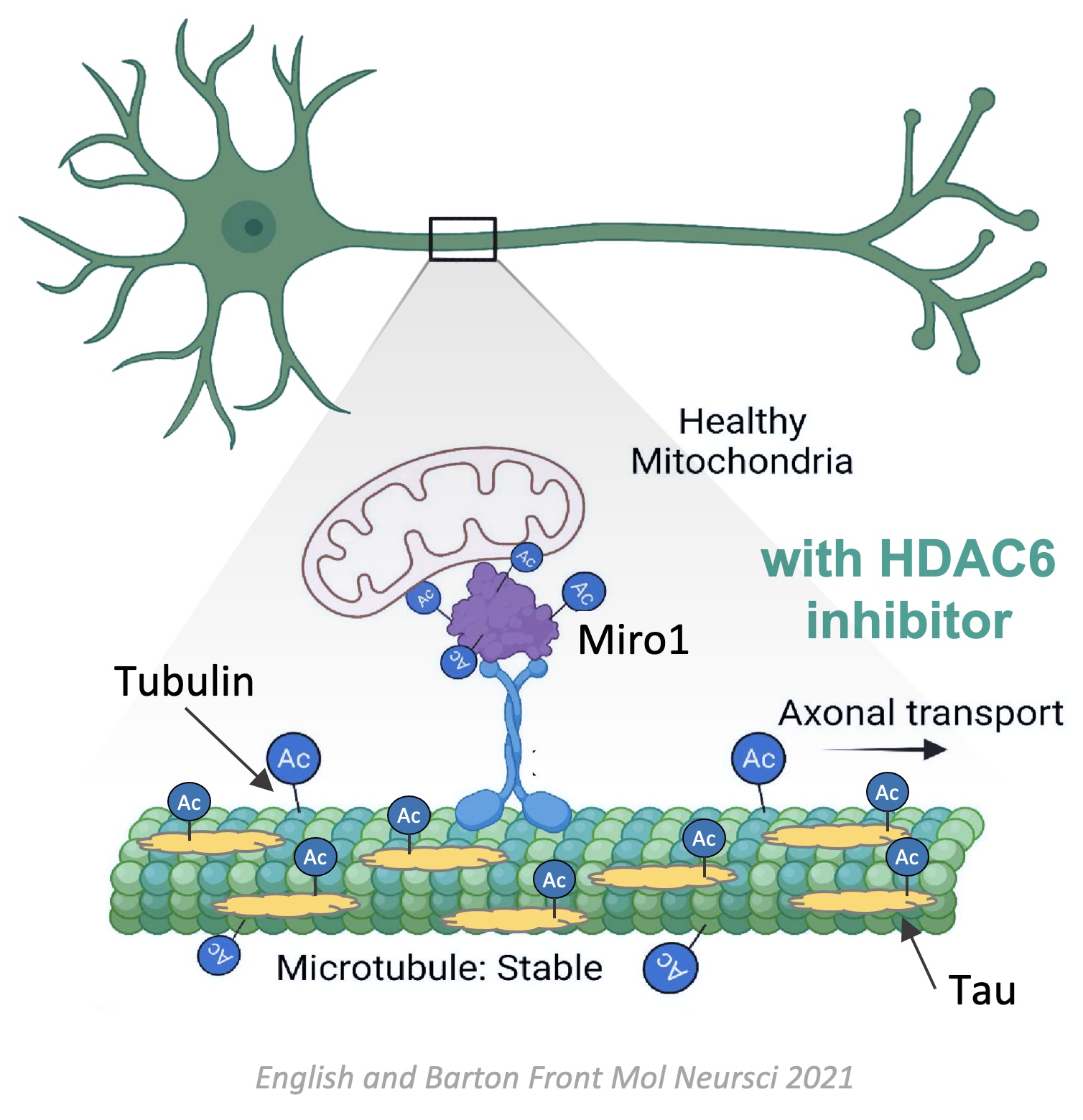
Increases acetylation of α-tubulin which strengthens the mechanical resilience of microtubules, improving transport of cargos along the microtubule
Increases acetylation of Miro1 which strengthens the linkage between mitochondria and motor proteins, increasing mitochondrial transport and function
Increases acetylation of tau which prevents tau hyperphosphorylation and subsequent neurofibrillary tangles and increases the degradation of pathological tau